On February 20, Antarctic sea ice likely reached its minimum extent of 1.99 million square kilometers (768,000 square miles), tying for second lowest extent in the 1979 to 2024 satellite record. This is the third consecutive year that Antarctic sea ice has reached a minimum below 2.0 million square miles (772,000 square miles).
Please note that this is a preliminary announcement. Changing winds or late-season melt could still reduce the Antarctic ice extent. NSIDC scientists will release a full analysis of the Antarctic and Arctic February conditions in early March.
Overview of conditions

Figure 1. Antarctic sea ice extent for February 20, 2024, was 1.99 million square kilometers (768,000 square miles). The orange line shows the 1981 to 2010 average extent for that day. Sea Ice Index data. About the data
Credit: National Snow and Ice Data Center
High-resolution image
On February 20, 2024, sea ice surrounding Antarctica reached an annual minimum extent of 1.99 million square kilometers (768,000 square miles), tying for second lowest minimum with 2022 in the 46-year satellite record. This year’s minimum is 850,000 square kilometers (328,000 square miles) below the 1981 to 2010 average Antarctic minimum extent of 2.84 millions square kilometers (1.10 million square miles). It is also 200,000 square kilometers (77,000 square miles) above the previous record low set on February 21, 2023. Nearly all of the remaining sea ice is in the Weddell Sea, Amundsen Sea, and the Southern Ocean off of Victoria Land, with isolated patches along the coasts of Enderby Land and Wilkes Land.
The Antarctic minimum extent was reached four days earlier than the 1981 to 2010 median date of February 24. The interquartile range for the date of the Antarctic minimum is February 20 to February 27.
Conditions in context
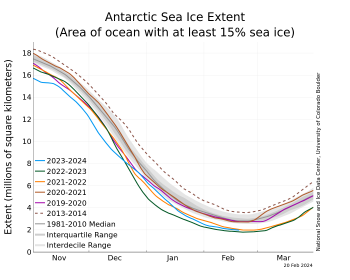
Figure 2a. The graph above shows Antarctic sea ice extent as of February 20, 2024, along with daily ice extent data for four previous years and the record high year. 2023 to 2024 is shown in blue, 2022 to 2023 in green, 2021 to 2022 in orange, 2020 to 2021 in brown, 2019 to 2020 in magenta, and 2013 to 2014 in dashed brown. The 1981 to 2010 median is in dark gray. The gray areas around the median line show the interquartile and interdecile ranges of the data. Sea Ice Index data.
Credit: National Snow and Ice Data Center
High-resolution image
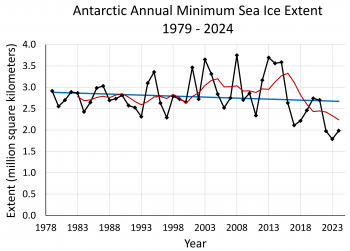
Figure 2b. This graph shows Antarctic annual sea ice minimum extent, depicted as black diamonds, from 1979 to 2024, based on a 5-day running average of daily extent. The linear trend line is in blue with a 1.7 percent per decade downward trend, which is not statistically significant. A five-year running average is shown in red.
Credit: W. Meier, NSIDC
High-resolution image
This year marks the third consecutive minimum Antarctic sea ice extent below 2.0 million square kilometers (772,000 square miles) (Figure 2a). The three minimums set in 2022, 2023, and 2024 are the three lowest in the 46-year record. Five of the lowest Antarctic sea ice extents have occurred since 2017 (see table below). With this series of low years, the trend in Antarctic minimum extent is negative and it is natural to speculate if this decline is significant. However, the period since 2017 is still too short to assess if these recent low extents indicate a clear decreasing signal; the magnitude of the trend is still small relative to the year-to-year variations in the ice cover. Note in this respect that 2013 through 2015 saw near record high minimum extents.
Overall, the downward trend in the annual Antarctic sea ice minimum extent computed over the complete satellite record is 4,700 square kilometers (1,800 square miles) per year, or 1.7 percent per decade relative to the 1981 to 2010 average. This trend is not statistically significant (Figure 2b). This is in stark contrast to the Arctic where the trend in the sea ice minimum is larger in magnitude and has strong statistical significance.
Five lowest minimum Antarctic sea ice extents (satellite record, 1979 to present)
| RANK | YEAR | MINIMUM ICE EXTENT | DATE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IN MILLIONS OF SQUARE KILOMETERS | IN SQUARE MILES | |||
| 1 | 2023 | 1.79 | 691,000 | Feb. 21 |
| 2 | 2022 2024 |
1.98 1.99 |
764,000 768,000 |
Feb. 25 Feb. 20 |
| 4 | 2017 | 2.11 | 815,000 | Mar. 3 |
| 5 | 2018 | 2.22 | 857,000 | Feb. 21 |
Values within 40,000 square kilometers (15,000 square miles) are considered tied.
For more information
NASA visualization of 2024 Antarctic sea ice minimum extent
NASA video of 2024 Antarctic sea ice minimum extent